Bitcoin: A Risky Bet or Fool’s Gold?
The Dark Side of Bitcoin: Why You Should Think Twice Before Investing in Bitcoin and other Cryptocurrencies
Introduction to Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, launched in 2009.
It allows peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries like banks.
While it’s gained popularity, Bitcoin carries significant risks for investors.
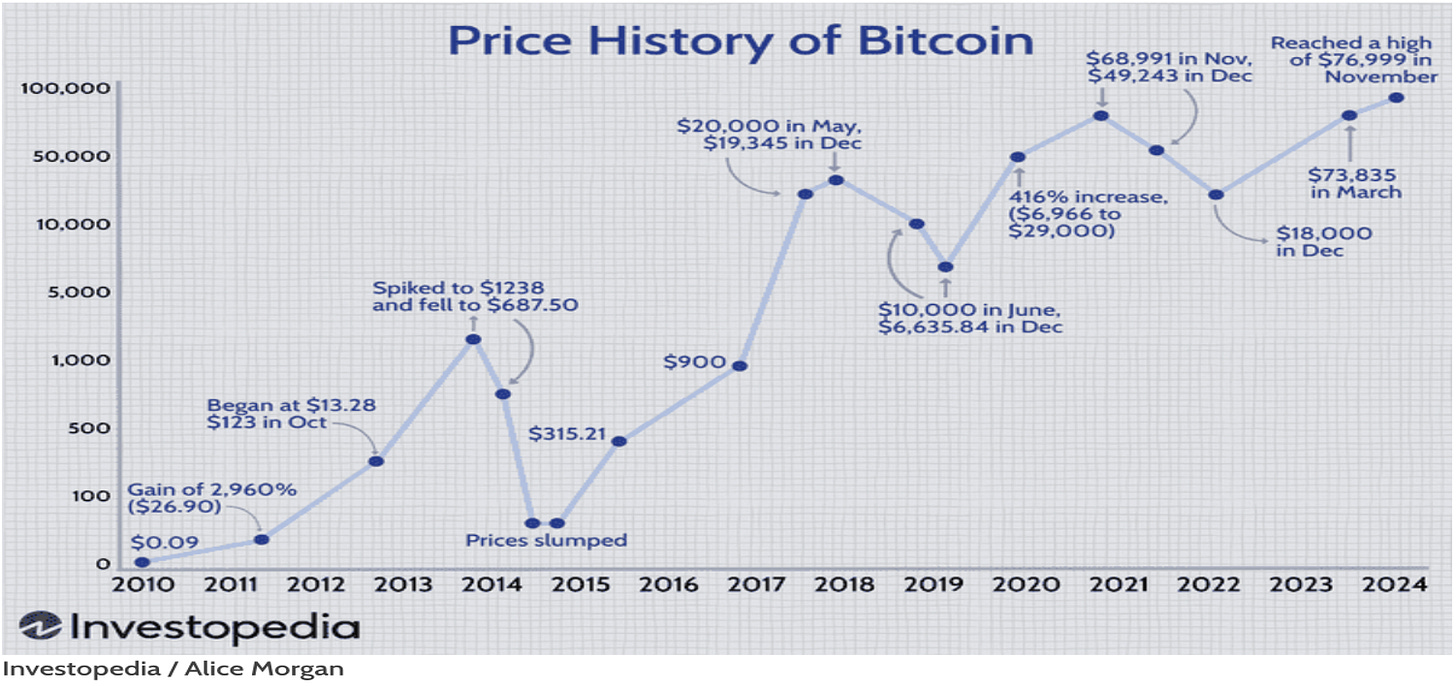
The Price Volatility of Bitcoin
Bitcoin prices are highly unpredictable.
Example: Between 2021 and 2022, the price of Bitcoin dropped close to 75% from its peak of $64,895 on April 14, 2021 to $16,530 by the end of 2022. However, since the beginning of 2023 It has been rising consistently and on January 21,2025 it touched a new high of $109,993 on Whitebit before settling to close at $106,749 on 22 January, 2025 .
Impact:
High risk for investors, especially those with low risk tolerance. Risk averse investors may not have the nerve to see the value of their capital declining more than 75% within few months and yet holding on to whatever is left in anticipation of a quick recovery.
Lack of Regulation
Bitcoin Operates Without Oversight
Bitcoin functions outside traditional financial systems.
Risks:
Fraud and scams.
Market manipulation.
No recovery options for lost or stolen funds.
Environmental Concerns
Bitcoin’s Environmental Impact
Bitcoin mining consumes enormous amounts of electricity.
Example:
Bitcoin’s energy usage is comparable to some small countries.
Mining relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to global warming.
Lack of Intrinsic Value
Bitcoin Lacks Intrinsic Value
Bitcoin is not backed by physical assets, companies, or governments.
Value is driven entirely by market speculation and manipulation.
Unlike stocks or bonds, it does not generate income or dividends.
Security Risks
Bitcoin’s Security Risks
Hacks and Theft:
Example: The 2014 Mt. Gox hack resulted in $450 million worth of Bitcoin being stolen.
Irreversible Transactions:
Mistakes or unauthorized transactions cannot be reversed.
Bitcoin Challenges and Limitations
Use Bitcoin Everywhere?
Problem: Bitcoin isn’t universally accepted as a payment method.
Explanation: While some companies accept Bitcoin, many retailers, service providers, and countries do not recognize it as legal tender.
Guarantee Price Stability
Problem: Bitcoin's value is highly volatile.
Explanation: Its price can swing dramatically within hours, making it impractical for stable transactions or as a store of value for risk-averse users.
Reverse Transactions
Problem: Bitcoin transactions are irreversible.
Explanation: If you send Bitcoin to the wrong address or fall victim to a scam, you can’t recover your funds.
Avoid Fraud Completely
Problem: Bitcoin transactions are pseudonymous, not anonymous.
Explanation: This makes scams, phishing, and other fraudulent activities common, and tracing funds can be difficult.
Operate Without Energy Costs
Problem: Bitcoin mining consumes enormous amounts of energy.
Explanation: It’s environmentally costly, making it impractical for sustainable use.
Avoid Taxation
Problem: Bitcoin transactions are not tax-free.
Explanation: Governments around the world are increasing regulations and requiring Bitcoin users to pay taxes on profits and usage.
Use Bitcoin Offline
Problem: You can’t transact Bitcoin without an internet connection.
Explanation: Bitcoin relies on the blockchain, which requires internet access to verify and complete transactions.
Scale for Mass Adoption
Problem: Bitcoin struggles with scalability.
Explanation: The network can handle about 7 transactions per second, compared to Visa’s 24,000+, making it slow and expensive for large-scale use.
Completely Avoid Regulation
Problem: Bitcoin is increasingly regulated.
Explanation: Many governments have introduced or are planning strict rules for Bitcoin, potentially limiting its use or affecting its price.
Avoid Centralization Completely
Problem: Bitcoin mining and control are concentrated in the hands of a few large players.
Explanation: This undermines the idea of decentralization.
President Donald Trump, Deregulations and Cryptocurrencies
Deregulation Efforts: Trump has initiated steps to ease regulations on the cryptocurrency industry, aiming to expedite its growth. This includes appointing crypto-friendly individuals to key positions, such as Paul Atkins as SEC chair and David Sacks as the crypto and AI czar. These moves signal his commitment to establishing the U.S. as a leading hub for cryptocurrency innovation. theguardian.com
Personal Ventures: Demonstrating personal involvement, Trump has launched his own cryptocurrency ventures, including a meme coin named $TRUMP. This direct participation underscores his endorsement of the crypto space and reflects a desire to capitalize on its popularity. theguardian.com
Political Strategy: During the 2024 election campaign, Trump became the first presidential candidate to accept digital assets as donations. He also proposed creating a federal "Bitcoin stockpile" from Bitcoins seized by the U.S. government or through new acquisitions. These actions indicate a strategic move to align with the growing crypto community and its supporters. Wikipedia
Advocacy for Innovation: By promoting cryptocurrencies, Trump positions himself as a proponent of technological advancement and financial innovation. This stance appeals to a segment of the electorate that values economic modernization and the potential benefits of decentralized finance.
It's important to note that while these initiatives aim to foster growth in the cryptocurrency sector, they have also drawn criticism. Concerns have been raised about potential ethical issues, investor safety, and the risk of corruption due to the unregulated nature of the crypto industry. theguardian.com
In summary, Trump's promotion of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies appears to be driven by a combination of economic, political, and personal interests, reflecting a significant shift in his approach to digital assets.
Bitcoin Speculation and Market Manipulation
Concerns about market manipulation in the cryptocurrency space have been associated with prominent figures and platforms, notably Michael Saylor of MicroStrategy and the exchange Binance.
Michael Saylor and MicroStrategy:
Michael Saylor, CEO of MicroStrategy, has been a vocal proponent of Bitcoin, leading his company to acquire substantial holdings of the cryptocurrency. As of recent reports, MicroStrategy holds around $48 billion worth of Bitcoin. WSJ
Critics, such as economist Peter Schiff, have accused Saylor of manipulating Bitcoin's price through these large-scale purchases. Schiff argues that MicroStrategy's significant acquisitions have artificially inflated Bitcoin's value, benefiting the company's stock price and Saylor's personal wealth. Bitget
Binance:
Binance, one of the world's largest cryptocurrency exchanges, has faced scrutiny over allegations of market manipulation. A 2024 report indicated that Binance terminated several members of its internal investigation team who were examining practices like pump-and-dump schemes and wash trading. The report also highlighted concerns about a VIP client, DWF Labs, allegedly engaging in activities that could manipulate market prices. Wikipedia
Additionally, Binance has acknowledged the prevalence of market manipulation tactics, such as order spoofing, within the cryptocurrency market. Order spoofing involves placing large buy or sell orders to create a false impression of demand or supply, only to cancel them before execution. binance.com
While both Michael Saylor and Binance have significantly influenced the cryptocurrency market, their actions have raised concerns about potential market manipulation. It's essential for investors to remain vigilant and conduct thorough research, recognizing that the crypto market can be susceptible to such practices.
Biggest Cryptocurrency Frauds
FTX and Sam Bankman-Fried
FTX, once a prominent cryptocurrency exchange, collapsed in 2022 due to extensive fraudulent activities orchestrated by its founder, Sam Bankman-Fried. The company misappropriated customer funds, leading to significant financial losses for investors. In March 2024, Bankman-Fried was sentenced to 25 years in prison after being convicted on multiple fraud and conspiracy charges. reuters.com
In August 2024, a U.S. court ordered FTX to pay $12.7 billion to compensate affected customers and fraud victims, marking the largest recovery in the Commodity Futures Trading Commission's history. theguardian.com
The FTX scandal underscores the critical need for stringent regulations and oversight in the cryptocurrency industry to protect investors and maintain market integrity.
Recent Developments in FTX Fraud Case theguardian.com
Bankrupt crypto exchange FTX ordered by US court to pay customers $12.7bn
Bitcoin Halving Manipulation
Bitcoin halving itself is not inherently a fraud, but some critics and skeptics argue that it can create opportunities for manipulation and misleading narratives within the cryptocurrency market. Let’s explore why some people view Bitcoin halving with skepticism or call it "fraudulent" in certain contexts:
1. Artificial Scarcity
What happens during halving?
•Bitcoin halving reduces the reward miners receive for mining new Bitcoin by half every four years.
•This is built into Bitcoin's code to control its total supply, which is capped at 21 million coins.
Criticism:
•Critics argue that halving artificially inflates demand by creating a perception of scarcity.
•This perceived scarcity is often used to promote Bitcoin as a “store of value,” leading to speculative buying and price surges.
2. Market Manipulation
How it happens:
•Prior to each halving, there is often a surge in marketing and hype around Bitcoin's price potential.
•Large holders (“whales”) or institutions may use the halving narrative to manipulate the market by creating artificial demand, then selling their holdings at a profit.
Impact:
•Retail investors often buy into the hype, expecting long-term gains, only to face significant losses when prices correct after the halving event.
3. Speculation vs. Fundamentals
Price Driven by Speculation:
•Historical data shows Bitcoin’s price often surges before and after a halving, but this is largely speculative rather than driven by real-world adoption or use.
Criticism:
•Detractors argue that halving events create unsustainable price bubbles that harm inexperienced investors.
•For example, Bitcoin’s price peaked after the 2016 and 2020 halvings but crashed significantly afterward.
4.Exaggerated Hype
Narrative of Guaranteed Returns:
•Bitcoin advocates often highlight how previous halvings led to price increases, creating a belief that this pattern will repeat indefinitely.
Reality Check:
•Past performance does not guarantee future results, and as Bitcoin matures, the market may not react as dramatically to future halvings.
5. Uneven Distribution of Wealth
Centralization of Wealth:
•A large percentage of Bitcoin is controlled by a small group of early adopters and institutional investors.
•Halving events disproportionately benefit these groups, as they are well-positioned to profit from price surges.
Criticism:
•Skeptics argue that halving perpetuates wealth inequality in the crypto space, making the system feel “rigged” for insiders.
Conclusion:
Bitcoin halving is not inherently fraudulent; it is a feature of Bitcoin's protocol designed to ensure controlled supply and scarcity. However, the narratives, speculative hype, and market manipulation that often surround halving events have drawn criticism. Retail investors should approach these events cautiously and critically evaluate the risks and rewards of investing based on halving expectations.
Alternatives to Bitcoin and Cryptocurrencies
Consider Safer Investments
Traditional Investments:
Stocks, bonds, ETFs, and real estate.
A diversified portfolio offers more stability and security.
Key Takeaway:
Bitcoin is volatile, lacks regulation, and has no intrinsic value.
Its environmental and security issues make it a risky investment.
Conservative and risk-averse investors should proceed with caution.
“Invest wisely and consider safer alternatives.”
Some important concerns and critical questions to ask yourself before you invest in Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrencies
1.Who Truly Controls Bitcoin?
Is Bitcoin truly decentralized, or are a few large players dominating the network
2.What Happens When Bitcoin Mining Stops?
After the 21 million Bitcoin limit is reached, how will miners stay incentivized?
3.Can Bitcoin Ever Become a Stable Currency?
With its volatility, can Bitcoin realistically replace traditional fiat currencies?
4.What About Environmental Concerns?
Can the Bitcoin network transition to greener energy sources?
5.Is Bitcoin Truly Secure?
With rising hacking incidents, how can Bitcoin protect user funds long-term?
6.Can Governments Kill Bitcoin?
If global regulations clamp down, can Bitcoin survive?
Disclaimer: Not Investment Advice
The information provided in this publication is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered financial, investment, or trading advice. While we strive to ensure accuracy, we do not guarantee the completeness or reliability of the information presented.
All investments involve risk, including the potential loss of capital. Past performance is not indicative of future results.You should conduct your own research and consult with a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions.
We do not act as a broker, dealer, or registered investment advisor. By accessing this content, you acknowledge and agree that any investment decisions you make are solely at your own risk.